how does a mass spectrometer work step by step|mass spectrometry explained simply : wholesaling Mass spectrometers always work with positive ions. Stage 2: Acceleration: The ions are accelerated so that they all have the same kinetic energy. Stage 3: Deflection: The ions are then deflected by a magnetic field according to their masses. Nuveen. Nuveen is an American asset manager and wholly owned subsidiary of financial planning firm TIAA, itself known for its legacy focus on managing money for not-for-profit .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webJogo. Descubra a grande e diversificada oferta de jogo do Casino Estoril. Da adrenalina da sala de jogos tradicionais às muitas emoções das salas mistas, passando pela acção non stop das modernas slot machines das salas de máquinas automáticas, é só escolher por onde começar a testar a sua sorte! 1.
Mass spectrometers always work with positive ions. Stage 2: Acceleration: The ions are accelerated so that they all have the same kinetic energy. Stage 3: Deflection: The ions are then deflected by a magnetic field according to their masses.
Stage 1: Ionization: Gas phase particles of the sample are ionized through a .IAL Chemistry: How does a mass spectrometer work (Its Steps and Uses) 1 Comment / IAL / By Tasvir Mahmood The Mass Spectrometer is a device used to identify different elements and compounds in a substance by finding out .Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Tandem Mass Spectrometry, usually referred to as MS/MS, involves the use of 2 or more mass analyzers. It is often used to analyze individual components in a mixture. This technique adds specificity to .
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
The 5 steps of LC/MS/MS. After preparation, samples are separated and concentrated in a liquid chromatography instrument (HPLC). . In the mass spectrometer, the quadrupoles filter separates ions based on their mass-to-charge ratios (m/z). Within the triple quadrupole configuration, the first quadrupole isolates analyte molecules, the second . What is mass spectrometry and how does mass spectrometry work? MS is a form of chemical analysis used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of atoms and/or molecules in a sample. It is also capable of distinguishing between different isotopes of the same element. . Figure 1: Outline of the main steps of MS and common variants available at . Hands-on Operation of an FTIR Spectrometer. Step 1: The first step is sample preparation. The standard method to prepare solid sample for FTIR spectrometer is to use KBr. About 2 mg of sample and 200 mg KBr are dried and ground. The particle size should be unified and less than two micrometers.
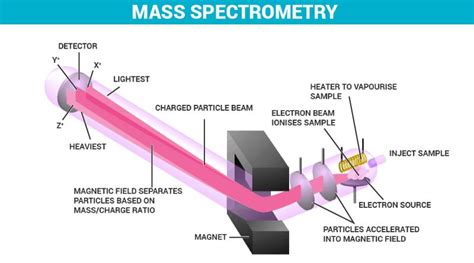
How Does a Mass Spectrometer Work? . The first step is getting the sample into the spectrometer, or sample introduction. The simplest method is to inject the sample through a special seal using a syringe needle. Any solvent used is . How Does Mass Spectrometry Work? Before you get started using mass spectrometry in biological research, you should make sure you understand the basics of how the technique works. There are three key stages to a mass spectrometer, and we discuss each in more detail below. 1. Ionization
A diagram of a magnetic sector mass spectrometer. Understanding what's going on. The need for a vacuum. It's important that the ions produced in the ionization chamber can travel from the ionizer, where they are created, through the mass filter, to the detector. The mean free path is the average distance a particle travels before it suffers a .
The extent of the deflection depends on the mass and charge of the ion. The lighter the mass of the ion, the more the deflection. Ions with a charge greater than +1 will also be deflected more. Detection: In this final stage, the beam of ions passing through the mass analyzer is detected by a detector on the basis of the mass-to-charge ratio (m . Mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics is the most comprehensive approach for the quantitative profiling of proteins, their interactions and modifications. It is a challenging topic as a firm grasp requires expertise in biochemistry for sample preparation, analytical chemistry for instrumentation and computational biology for data analysis. In this short guide, . Dempster’s spectrometer utilized only a magnetic field, which deflected the ion beam through an arc of 180°. In Dempster’s machine, an ion beam homogeneous in mass and energy but diverging from a slit could be brought to a direction focus. This spectrometer was employed by Dempster to make accurate determinations of the abundances of the isotopes of .Mass Spectrometry - A Textbook will guide them from their first steps to the successful application of mass spectrometry in their daily work in research. Starting from the very principles of gas phase ion chemistry and isotopic properties, it leads through the design of mass analyzers and ionization methods in use to mass spectral .
2. Acceleration: The generated ions are then accelerated by an electric field, causing them to move towards a detector.. 3. Deflection: In the presence of a magnetic or electric field, the ions are deflected based on their mass-to-charge ratio.Heavier ions are deflected less than lighter ions. 4. Detection: The ions are detected based on their mass-to-charge ratio, and the .
what is mass spectrometry commonly used for
Mass spectrometry (MS) - Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. Mass spectrometry (MS) is the study of ions created as a result of ionization/fragmentation as .
Single quadrupole GC-MS. When gas chromatography is combined with a mass spectrometer that includes just one quadrupole, it is often referred to simply as GC-MS. GC-MS is well suited to the everyday analysis of samples where .The mass spectrometer acts not only as the “LC detector” but, at least in principle, it provides the capability to identify the species corresponding to each chromatographic peak through its unique mass spectrum. Figure 1.1: The power of the LC-MS technique to separate and identify each component of aThe practice of simultaneous MS is frequently termed tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS or MS 2) and refers to two or more reaction steps being performed on selected ions. In the first step of mass analysis, precursor ions are formed in the ion source and induced to fragment. In the second step, the fragmentation products are detected and analyzed.
A mass spectrometer can measure the mass of a molecule only after it converts the molecule to a gas-phase ion. To do so, it imparts an electrical charge to molecules and converts the resultant flux of electrically charged ions into a proportional electrical current that a data system then reads.
A mass spectrometer is a device used to perform this measurement. The first mass spectrometer was built in 1912 by J.J. Thomson. Originally called a parabola spectrograph, the device was used to provide definitive evidence of nonradioactive isotopes. Through the years, the mass spectrometer has become one of the most useful devices found in .The second step is the time-of-flight mass spectrometry phase. In the linear mode, particles will impinge upon the linear detector within a few nanoseconds after ionization. Higher mass molecules will arrive later than lighter ones. Flight time measurement makes it possible to determine molecule masses directly. The sample mixture is first separated by the GC before the analyte molecules are eluted into the MS for detection. 1 They are transported by the carrier gas (Figure 1 (1)), which continuously flows through the GC and into the MS, where it is evacuated by the vacuum system (6). 1. The sample is first introduced into the GC manually or by an autosampler (Figure 1 (2)) .Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique in which samples are ionized into charged molecules and ratio of their mass-to-charge (m/z) can be measured. In MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, the ion source is matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI), and the mass analyzer is time-of-flight (TOF) analyzer.
How does Gas Chromatography-Mass spectrometry work? The first step in the analysis is the gas chromatograph, where a capillary column coated with a stationary (liquid or solid) phase separates the sample into its constituent components after efficiently vaporizing it into the gas phase. An inert carrier gas, such as helium, hydrogen, or .How does a mass spectrometer work? A mass spectrometer is an important analytical instrument which scientists can use to identify the amount and type of different chemicals in a substance. In this explanation I’ll go through how the mass spectrometer works. . or describe how a particular step works, before then going on to interpret a mass .The instrument used in this experiment is an Agilent 6890N GC/MS (low-resolution mass spectrometer) pictured in Figure 5.2. The mass spectrometer and GC are controlled by Chemstation software on the computer. This instrument can be found in room 3475. Figure 5.2: GC/MS Instrument used in this experiment.
How did a Spectrophotometer help scientists identify a species of bacteria that can clean up pollution? What is a Spectrophometer anyway, and how do you use .
mass spectrophotometer diagram
Jeux gratuits de roulette en ligne. De nos jours, les jeux gratuits de roulette existent en .
how does a mass spectrometer work step by step|mass spectrometry explained simply